Reverse osmosis is the most complete and effective filtration method available today. It is also the most common water treatment method used by producers of bottled water. It is effective in removing or significantly reducing a very broad spectrum of contaminants. Of all available technologies used for water treatment for domestic purposes, reverse osmosis guarantees the most effective water purification. Reverse osmosis makes it possible to remove particles as small as single ions from water. The holes in an osmotic membrane have a size of about 0.0005 microns (note that bacteria have a size of 0.2 to 1 micron, and viruses from 0.02 micron to 0.4 micron).
There are two types of osmotic membranes used for domestic purposes:
- Thin Film Composite (TFC)
- Cellulose triacetate (CTA)
While TFC membranes have a significantly higher removal rate than CTA membranes, they are more susceptible to wear through chlorine absorption. Therefore, it is important to use an activated carbon filter as a pre-filter to remove excess contaminants. A typical reverse osmosis system consists of a carbon initial filter (GAC), an osmotic membrane, a clean water storage container and a faucet that delivers purified water. Reverse osmosis systems differ mainly in the quality of the membrane, efficiency (number of ounces of filtered water per hour) and size of the pure water storage container.
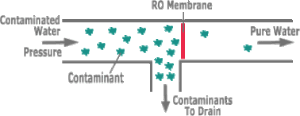
Reverse osmosis uses a semi-permeable membrane that allows pure water molecules to pass through, trapping impurities too large to pass through its micropores. Good quality osmotic systems use a process called crossflow, which allows the membrane to self-clean.
The water does not flow into the membrane, but flows “over it” so that the impurities held in the membrane are taken away along with the contaminated water. The reverse osmosis process requires a force that pushes the water through the membrane, but the water pressure in the tap is sufficient for the process to take place effectively.
Reverse osmosis is an excellent choice for home water filtration applications. It is the most recommended solution for tap water treatment. Reverse osmosis is very effective, however, we do not recommend the use of osmotic membrane as the only filtration media for water that may contain biological contaminants as in the case of well or lake water. For these applications, we advise the use of a two-stage filter combining an osmotic membrane and an ultraviolet lamp / filter (to be discussed later) connected to the home main water source. This way we get the best protection against bacteria and viruses. Keeping in mind that the osmotic membrane can wear out very quickly due to chlorine, iron, hydrogen sulfide or bacteria, it is a good idea to use a sediment pre-filter and a carbon pre-filter. This way the impurities caught by the pre-filters will not clog the osmotic membrane. In case your water is very hard, home water softening filters should be applied. This will also prolong the lifetime of our filter.
Fact: water obtained by reverse osmosis is very healthy and beneficial for people. People often wonder if Reverse Osmosis is…
Fact: Reverse Osmosis, despite its name, is very well-filtered water. Some people will try to tell you that reverse osmosis…
Fact: Reverse osmosis removes inorganic minerals from water that are unhealthy. A reverse osmosis filter does remove minerals from tap…
Fact: A reverse osmosis filter provides water that cannot suck minerals out of the human body. This is another method…
Fact: Reverse Osmosis generates slightly acidic or neutral water. It is not unhealthy! Reverse osmosis systems can actually lower the…
Fact: Reverse Osmosis uses a lot of water, but that water can be reused. Of all the false opinions about…
Fact: Reverse Osmosis system is affordable This myth may actually be true as our financial circumstances determine our point of…
- Myth 7: Reverse Osmosis Is Too Expensive
- Myth 6: Reverse Osmosis Wastes a lot of Water
- Myth 5: Reverse Osmosis generates very acidic water with low pH
- Myth 4: Reverse Osmosis Sucks Minerals Out of Body
- Myth 3: Reverse Osmosis Removes Healthy Minerals From Water
- Myth 2: Reverse Osmosis is a NASA technology.
- Myth 1: Reverse Osmosis Produces Unhealthy Water
